The success of an organisation largely depends on the people who run it. Promotions is a powerful strategy for motivating employees.
Employee promotion serves as a crucial milestone, symbolizing growth, recognition, and new opportunities. It is a moment when hard work and dedication are acknowledged, and individuals are entrusted with increased responsibilities. But promotion is not just a mere change in job title; it carries significant implications for both employees and organisations alike.
But how can you determine who deserves a promotion?
The decision to promote cannot be taken lightly. The art of promotion necessitates the careful evaluation of a variety of factors, ranging from performance to potential. Promotion establishes the recognition of employees’ hard work and dedication toward their job.
In this blog, we will highlight the types and importance of promoting employees. We will also look at different tactics you can use to promote employees.
What Is Employee Promotion?
Employee promotion refers to the advancement of an employee to a higher position within an organisation. It is a process by which an individual is given increased responsibilities, authority, and possibly a higher salary or benefits package. Employee promotions are typically based on merit, performance, skills, experience, and potential.
Promotions can occur at the same job level. Here, an employee takes on additional responsibilities and becomes a senior member of their current team. They can also involve moving to a higher job level, like being promoted from a junior position to a managerial role.
Types of Employee Promotion
Types of employee promotions may vary between organisations based on their structure, policies, and career development programs.
However, basically, there are three different types of employee promotions that can occur within an organisation.
1. Vertical Promotion
Vertical promotions provide employees with more or different responsibilities, a higher salary, and a new job title. This is what most people envision when they consider promotions. Vertical promotions are an excellent way to reward high-performing employees and fill open jobs that might benefit from an internal perspective. They also communicate to your employees that the organisation values their professional development.
2. Horizontal Promotion
Horizontal promotions entail an increase in salary and a new title, but the actual position remains the same. These promotions are effective in rewarding loyalty, recognizing new skills, and increasing retention. An example of horizontal promotion is when in universities, lecturers become senior lecturers after five to seven years.
3. Dry Promotion
Dry promotions involve all the responsibility of a new title, but without the benefits that come with it. In other words, the company will ask more of the employee but will not provide compensation in return.
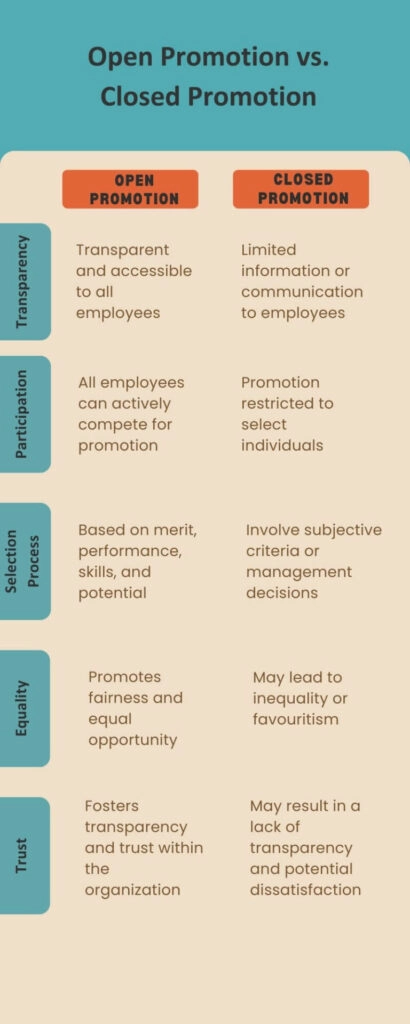
4. Open vs. Closed Promotion
All of the above promotion types are classified as either open or closed employee promotions.
Open promotion refers to a promotion process that is transparent and accessible to all employees within an organisation. Here, the organisation communicates the promotion criteria, qualifications, and requirements to all employees. It allows them to actively participate and compete for promotion opportunities. The selection process is typically based on merit, performance, skills, experience, and potential.
On the other hand, closed promotion is a process where the promotion opportunities are limited to predetermined candidates. Here, the organisation may choose to promote employees based on subjective criteria or decisions made by management. However, the employers do not openly communicate the promotion process to all employees.
Benefits of Employee Promotion
Promoting employees creates a win-win situation for both the organisation and the individuals involved. It fosters a positive work environment, enhances employee satisfaction and loyalty, drives productivity, and contributes to long-term organisational success.
Let us discuss the advantages of promoting employees:
1. Retention of Top Talent
Promoting employees from within the organisation is an effective strategy for retaining top talent.
According to a study by LinkedIn, internal promotion reduces employee turnover by 61%.
When employees see clear paths for advancement, they are more likely to stay with the organisation, reducing turnover. By offering promotion opportunities, organisations can cultivate a sense of loyalty and commitment among their employees, fostering long-term relationships.
2. Increase Motivation and Engagement
Promotions recognize and reward employees’ hard work and achievements, boosting their motivation and job satisfaction. It instills a sense of pride and accomplishment, leading to increased engagement and dedication to their roles and the organisation.
Promotions can have a positive impact on overall morale and team dynamics. They inspire other employees to work hard and strive for advancement opportunities, creating a culture of growth. It fosters a positive work environment and enhances teamwork and collaboration.
3. Talent Development and Succession Planning
The Corporate Leadership Council found that organisations that effectively promote from within have 20% higher employee performance.
Promoting employees allows organisations to nurture and develop their talent pool, ensuring a pipeline of capable individuals for higher-level positions. It facilitates succession planning, mitigates talent gaps, and reduces the time and resources required for external recruitment and onboarding.
4. Enhance Skills and Knowledge
Promotions often involve new responsibilities and challenges, allowing employees to develop and enhance their skills. Employees gain a broader skill set, expand their knowledge base, and become more versatile. It ultimately benefits both their current and future roles within the organisation.
When to Promote Employees?
There is no right or wrong time to promote an employee. Most of the time, it depends on the position, experience, and abilities of an employee. Some positions may require certain experience, whereas others may require a longer tenure with the company. To give you an idea, here are some points that you can remember while deciding when to promote an employee:
- Consistent demonstration of exceptional performance and track record of delivering high-quality work
- Develop new skills required for the higher-level position or the specific needs of the organisation.
- Take on new responsibilities to handle higher-level tasks
- Showcase ability to motivate and mentor others
- Exhibit a positive attitude, a strong work ethic, and commitment to the company’s mission.
- Manage themselves and require little supervision.
- Hold themselves accountable for their tasks.
- Learns and unlearns to adapt to change
How to Promote Employees?
Promoting an employee involves a thoughtful and strategic approach to ensure a fair and successful transition to a higher-level position. Here is a detailed explanation of the steps involved in promoting an employee:
1. Assess the Need for Promotion
Determine the specific need or rationale for the promotion. Identify if there is a vacancy in a higher-level position or if the employee has demonstrated exceptional performance. You can also check if their skills align with a new role that has been created within the organisation.
2. Define Promotion Criteria
Clearly define the criteria for promotion, including the skills, competencies, experience, and performance indicators required for the higher-level position. Establish measurable and objective benchmarks that the employee needs to meet to be considered for promotion.
3. Identify Potential Candidates
Evaluate the pool of potential candidates based on their performance, skills, and alignment with the promotion criteria. Consider both internal and external candidates but prioritize internal talent to promote career growth and retain top performers.
4. Provide Feedback:
Engage in open and transparent communication with the employee regarding their potential for promotion. Provide constructive feedback on their strengths and areas for development. You can also offer guidance on how they can improve their chances of being promoted.
5. Conduct a Performance Evaluation:
Conduct a thorough performance evaluation of the employee based on the established criteria. Assess their achievements, contributions, and growth in their current role. Gather feedback from relevant stakeholders, including supervisors, peers, and subordinates, if applicable.
6. Assess via projects and interviews:
Depending on the organisation’s promotion process, conduct interviews or assessments to evaluate the employee’s suitability for the higher-level position. This may involve panel interviews, behavioral assessments, case studies, or presentations.
7. Review and Select:
Evaluate all the information gathered, including performance evaluations, feedback, and interview and assessment results, to make an informed decision. Consider input from relevant stakeholders, such as department heads or senior management, if necessary.
8. Generate an Offer:
Once the decision is made to promote an employee, extend a formal offer to employees. It should include details about the new position, salary, benefits, and any other pertinent information. Provide support and guidance during the transition period to ensure a smooth onboarding process.
9. Communicate and Recognise:
Announce the employee’s promotion to the organisation, emphasizing their accomplishments, skills, and readiness for the new role. Celebrate the employee’s success and recognize their promotion publicly to boost morale and motivate other employees.
Conclusion
Employee promotion is a tricky aspect of organisational performance management, but it is also quite manageable. It is important to understand that deciding if an employee should be promoted or which one to promote can be difficult. So, do not rush; take your time and evaluate all the relevant information before reaching an educated conclusion.











